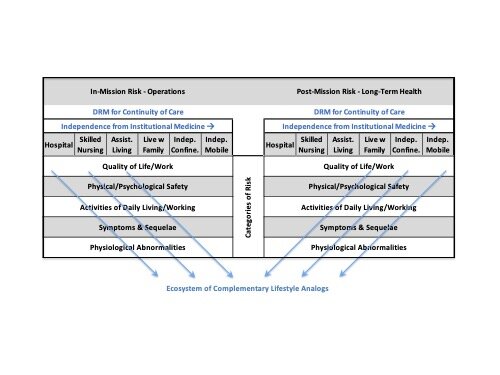
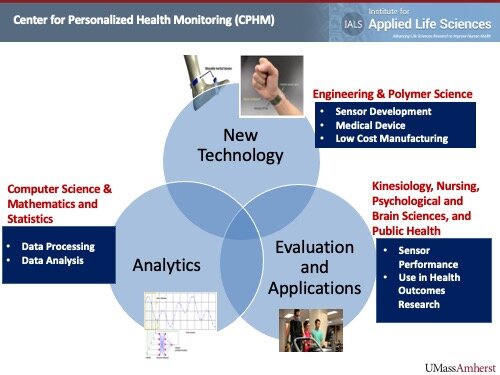
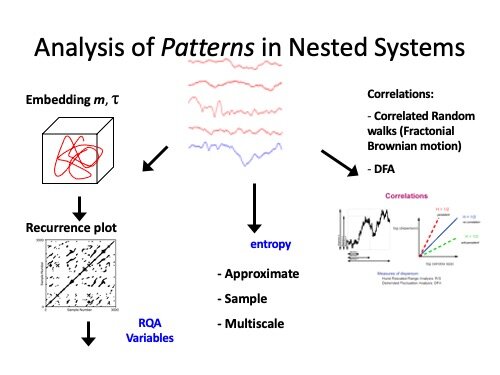
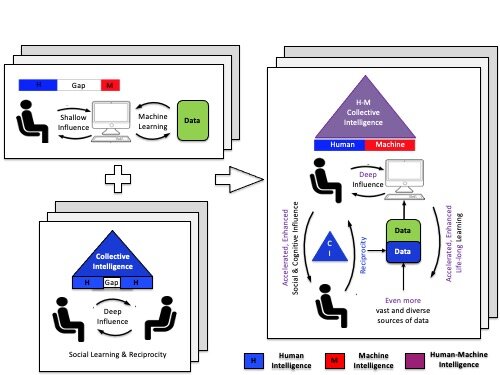
Crowd Systems Engineering
The various instantiations of crowd-based approaches can be instructive in more general strategies for open innovation. These recent developments reveal that increasingly we are experiencing innovation in innovation itself, and much of this is about the various communities that influence innovation. A more strategic and architectural view of expeditionary communities is required in our time.
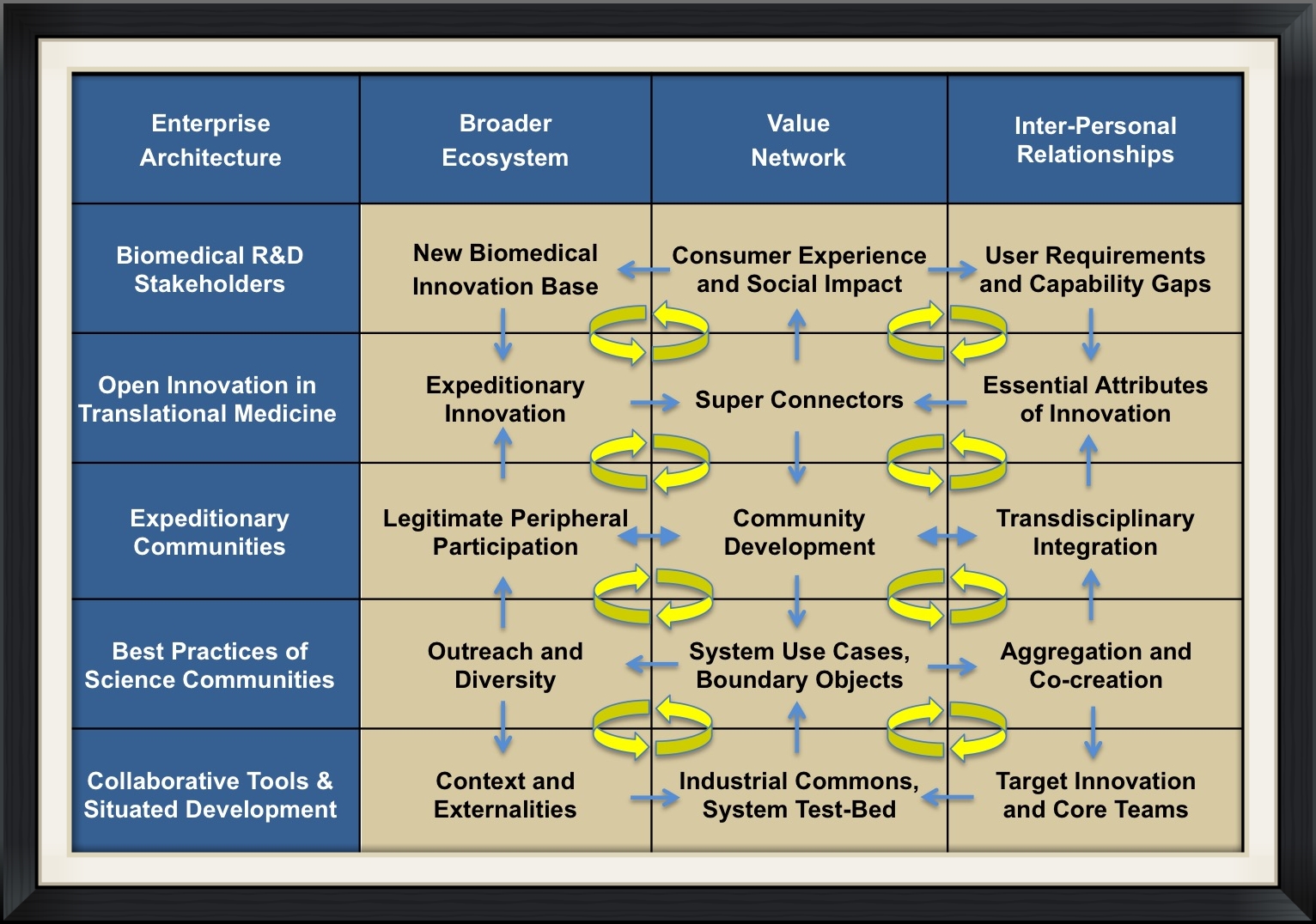
Enterprise Architecture for Selective Open Innovation
Sociotechnical abstraction hierarchies can be useful in the definition and measurement of such causal structure in enterprises that don’t have a well-defined a priori structure or that have the freedom to evolve significantly from their initial conditions (adhocracies). These abstraction hierarchies situate all participants in a social and technical context. This is especially valuable in novel situations that require adaptation and convergence on an observably stable state. We believe that the abstraction hierarchy is a promising tool for developing a dynamic evidence-based framework to coordinate pre-scientific and pre-money business progress toward expeditionary innovation.

Levels of Abstraction in Translational Medicine
Levels of abstraction visualized as stacks in an enterprise architecture
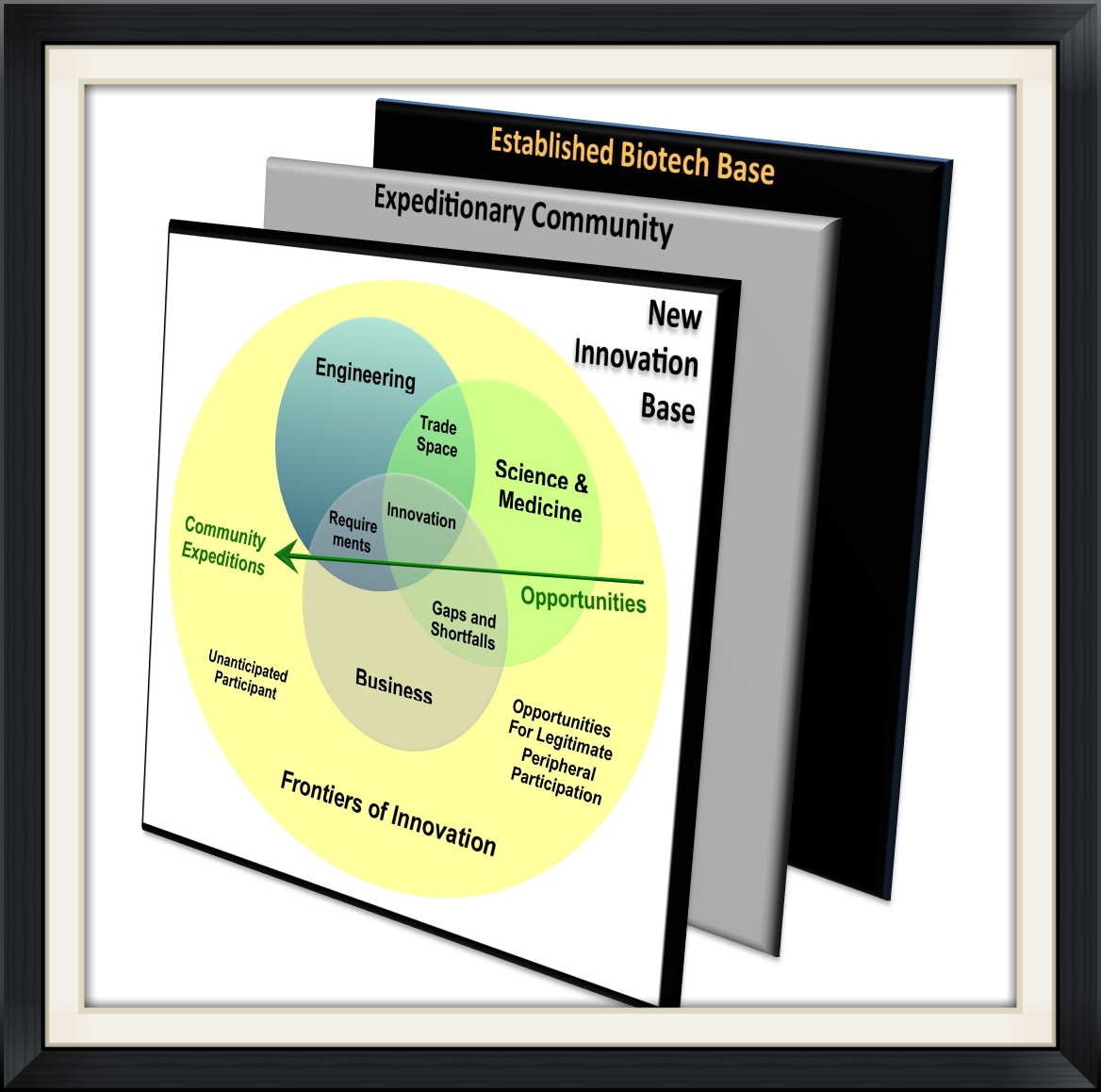
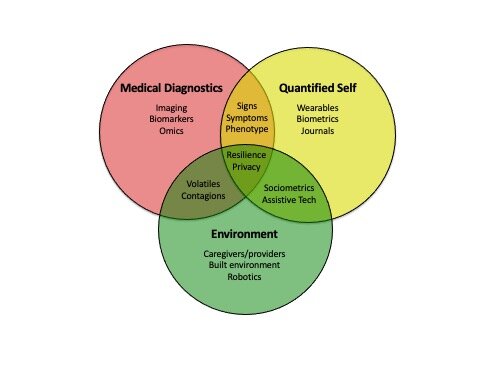
Levels of Decomposition in Translational Medicine
Levels of decomposition visualized as cross-cutting stacks in an enterprise architecture.

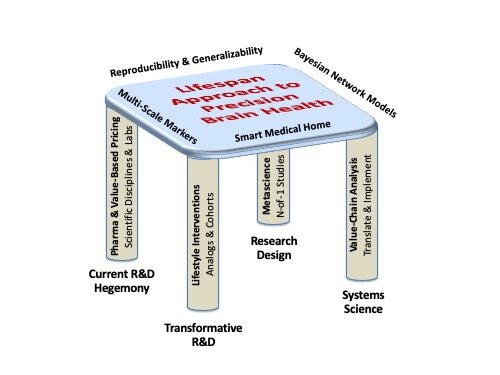
Expeditions of Innovation in Translational Medicine
Expeditions that can be organized through a sociotechnical enterprise architecture
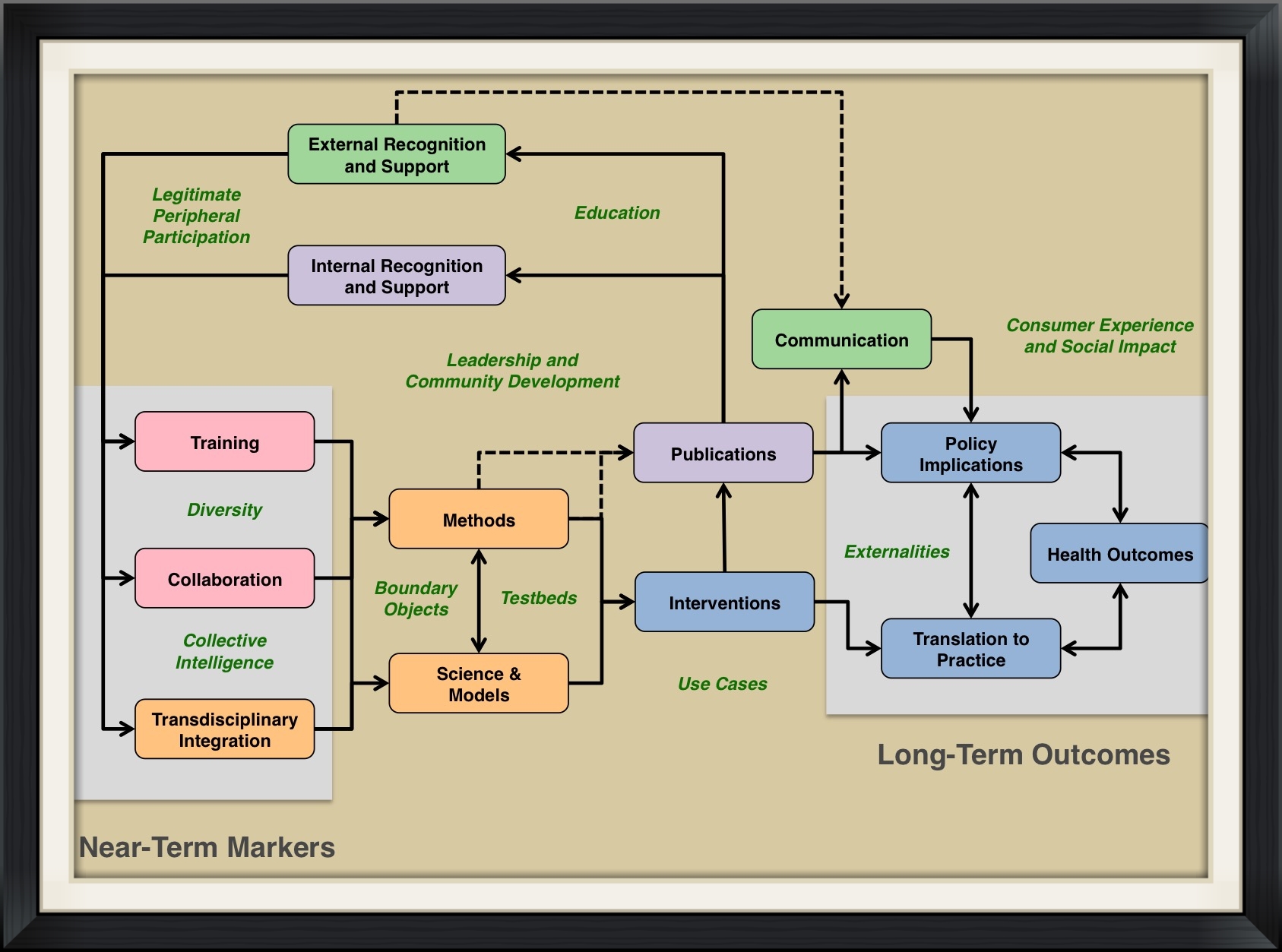
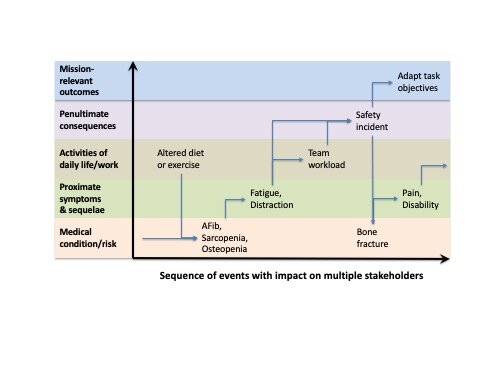
Logic Model for Translational Medicine
Logic model adapted from Trochim et al. (2008) for translational science that enables program managers to track markers of success in a transdisciplinary team.
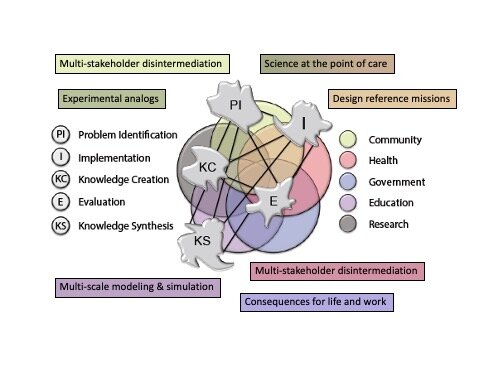
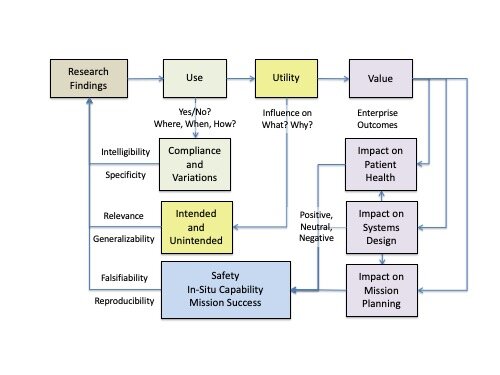
Kitson's Complexity Network Model for Knowledge Translation (modified)
Kitson, A., Brook, A., Harvey, G., Jordan, Z., Marshall, R., O’Shea, R., & Wilson, D. (2018). Using complexity and network concepts to inform healthcare know (adapted with permission of Alison Kitson)